Symmetrical Component Analysis
Decoding Unbalanced Systems • Enhancing Fault Diagnosis • Empowering Grid Stability
Decoding Unbalanced Systems • Enhancing Fault Diagnosis • Empowering Grid Stability
Symmetrical Component Analysis is a powerful technique used to simplify the study of unbalanced three-phase systems. It breaks down complex, asymmetrical voltages or currents into three balanced sets: positive-sequence, negative-sequence, and zero-sequence components.
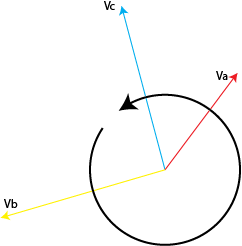
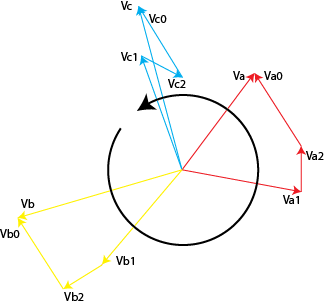
This component represents a balanced set of phasors rotating in the same direction as the original system. It reflects normal operating conditions and is used in load flow and stability analysis.
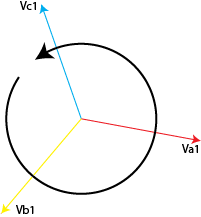
The negative-sequence component rotates in the opposite direction and arises from faults or unbalanced loads. It can cause heating and torque pulsations in motors and generators.
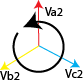
This component consists of phasors that are equal in magnitude and phase. It typically appears in ground faults and is critical for protective relay coordination.